Relay Configuration¶
For security reasons, clients may wish to avoid exposing a machine to the internet that has direct access to confidential assets which need to be transferred. In this case, a Relay server can be used as proxy sitting in between the JetStream server and the internet.
A Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) is a computer that has access to the internet but not to the private network. A firewall sits between the DMZ and the private network that forbids any incoming connections from being accepted into the private network, thereby preventing any would-be attackers from accessing this network, even if the DMZ should be compromised. By contrast, the firewall allows incoming connections to the DMZ from the private network.
Using the topology outlined in this article, a Relay server is run in the DMZ. Before sending or receiving assets, the JetStream server in the private network is configured to route all data through this Relay. The Relay server simply forwards data from the JetStream server to its external internet connection. Since all data is encrypted by the JetStream server before it is sent to the Relay, the DMZ never has access to unencrypted assets. This topology works because the JetStream server initiates the connection with the Relay and is therefore permitted through the firewall between the DMZ and the private network.
Requirements¶
The relay service is installed along with the server service, but it is not started by default. It can be started using standard OS system service commands.
The relay server opens TCP port 8887 and listens for connections from a JetStream server. It then opens UDP ports on behalf of the server. Typically this means that the JetStream server needs to be able to connect to the relay server on 8887/TCP. The relay server then needs to be able to open ports to the external internet, such as the standard JetStream server ports of 8886/TCP and 8886/TCP. It is the relay, not the server, that needs a static IP address and firewall port forwarding rules in this case.
Single Relay¶
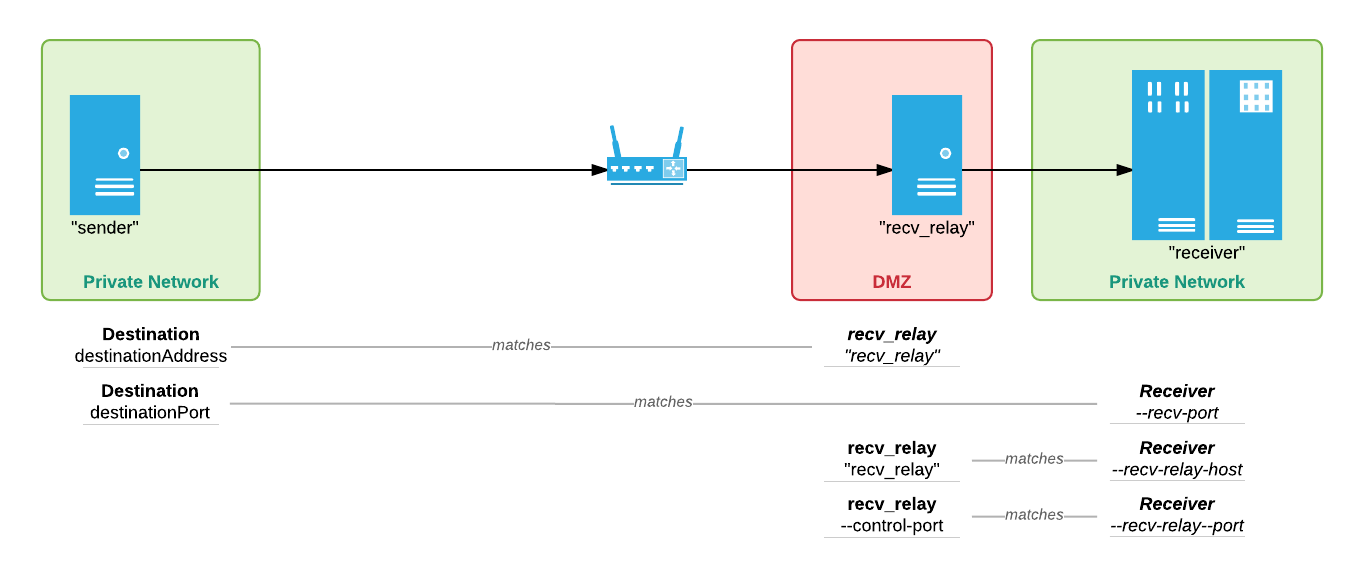
Here, a relay is assigned in the DMZ in front of the Receiver. This allows clients to send files to the Receiver’s network, without exposing the Receiver’s file system or network to a public connection.
Receiver Relay¶
To start the Receiver Relay, specify the TCP control port to which the Receiver will connect:
[recv_relay]# jetstream relay_server --control-port=8887
- The
jetstream relay_server --control-portvalue will be used to configure thejetstream server --recv-relay-portfor the Receiver.
Receiver¶
To start the Receiver, specify the hostname and TCP control port for the Receiver Relay.
[receiver]# jetstream server --recv-relay-host=recv-relay --recv-relay-port=8887 --recv-port=8886
- The
jetstream server --recv-relay-hostvalue must match the hostname or ip of the Receiver Relay.- The
jetstream server --recv-relay-portvalue must match thejetstream relay_server --control-portspecified for the Receiver Relay.- The
jetstream server --recv-portvalue will be used to configure thedestinationPortspecified for the Destination.
Transfer¶
To create a Destination for this configuration, specify the Receiver Relay hostname and Receiver UDP port.
>>> createDestination(destinationAddress='recv_relay', destinationPort=8886)
- The
destinationAddressmust match the hostname or ip of the Receiver Relay.- The
destinationPortmust match thejetstream server --recv-portspecified for the Receiver.
Note that the ‘relayAddress’ and ‘relayPort’ parameters are not specified for the Destination. These are specified only if a transfer is routed through a Sender Relay; this configuration does not use a Sender Relay.
Double Relay¶
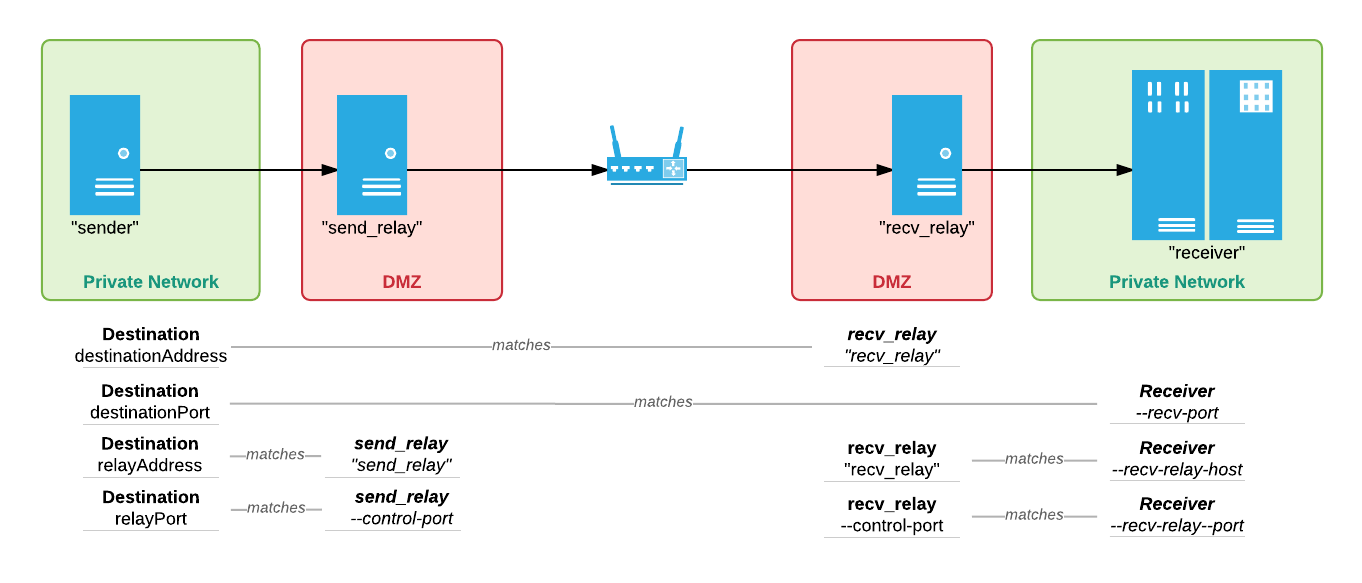
Here, two relays are assigned in the DMZ in front of each of the Sender and Receiver. This allows clients to send files to the Receiver’s network, without exposing the file systems or networks from either the Sender or Receiver to a public connection.
Receiver Relay¶
To start the Receiver Relay, specify the TCP control port to which the Receiver will connect:
[recv_relay]# jetstream relay_server --control-port=8887
- The
jetstream relay_server --control-portvalue will be used to configure thejetstream server --recv-relay-portfor the Receiver.
Receiver¶
To start the Receiver, specify the hostname and TCP control port for the Receiver Relay.
[receiver]# jetstream server --recv-relay-host=recv_relay --recv-relay-port=8887 --recv-port=8886
- The
jetstream server --recv-relay-hostvalue must match the hostname or ip of the Receiver Relay.- The
jetstream server --recv-relay-portvalue must match thejetstream relay_server --control-portspecified for the Receiver Relay.- The
jetstream server --recv-portvalue will be used to configure thedestinationPortspecified for the Destination.
Sender Relay¶
To start the Sender Relay, specify the TCP control port through which a Destination will route a transfer:
[send_relay]# jetstream relay_server --control-port=8887
- The
jetstream relay_server --control-portvalue will be used to configure therelayPortfor the Destination.
Destination¶
To create a Destination for this configuration, specify the Receiver Relay hostname and Receiver UDP port. Additionally specify the hostname and control port for the Sender Relay.
>>> createDestination(destinationAddress='recv_relay', destinationPort=8886, relayAddress='send_relay', relayPort=8887)
- The
destinationAddressmust match the hostname or ip of the Receiver Relay.- The
destinationPortmust match thejetstream server --recv-portspecified for the Receiver.- The
relayAddressmust match the hostname or ip of the Sender Relay.- The
relayPortmust match thejetstream relay_server --control-portspecified for the Sender Relay.